How The Universe Is Way Bigger Than You THINK? – News Editor ...
Did you know that our star, the Sun, is just one of hundreds of billions of stars swirling within an enormous cosmic place called the Milky Way Galaxy?
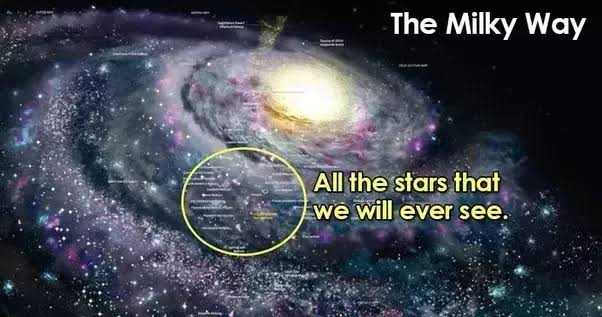
Without a telescope , we can see about 6,000 stars from Earth. That may seem like a lot of stars, but it’s actually only a small part of the whole. If you think of the entire galaxy as a giant pizza, all the stars you can see from Earth fall within about one pepperoni on that pizza. In fact, for every star you can see, there are more than 20 million you cannot see. Most of the stars are too faint, too far away or blocked by clouds of cosmic dust.Our Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. Within it, there are at least 100 billion stars, and on average, each star has at least one planet orbiting it. … Our Sun is one of at least 100 billion stars in the Milky Way
The Universe is everything we can touch, feel, sense, measure or detect. It includes living things, planets, stars, galaxies, dust clouds, light, and even time. Before the birth of the Universe, time, space and matter did not exist.
This is what the Milky Way Galaxy looks like from Earth. Have you seen it in the night sky?Our Milky Way Galaxy is just one of billions of galaxies in the universe. Within it, there are at least 100 billion stars, and on average, each star has at least one planet orbiting it. … Our Sun is one of at least 100 billion stars in the Milky WayThe Universe contains billions of galaxies, each containing millions or billions of stars. The space between the stars and galaxies is largely empty. However, even places far from stars and planets contain scattered particles of dust or a few hydrogen atoms per cubic centimeter. Space is also filled with radiation (e.g. light and heat), magnetic fields and high energy particles (e.g. cosmic rays).
The Universe is incredibly huge. It would take a modern jet fighter more than a million years to reach the nearest star to the Sun. Travelling at the speed of light (300,000 km per second), it would take 100,000 years to cross our Milky Way galaxy alone.
Without a telescope , we can see about 6,000 stars from Earth. That may seem like a lot of stars, but it’s actually only a small part of the whole. If you think of the entire galaxy as a giant pizza, all the stars you can see from Earth fall within about one pepperoni on that pizza. In fact, for every star you can see, there are more than 20 million you cannot see. Most of the stars are too faint, too far away or blocked by clouds of cosmic dust.No one knows the exact size of the Universe, because we cannot see the edge – if there is one. All we do know is that the visible Universe is at least 93 billion light years across. (A light year is the distance light travels in one year – about 9 trillion km.)
The Universe has not always been the same size. Scientists believe it began in a Big Bang, which took place nearly 14 billion years ago. Since then, the Universe has been expanding outward at very high speed. So the area of space we now see is billions of times bigger than it was when the Universe was very young. The galaxies are also moving further apart as the space between them expands.
All the individual stars we see in the night sky are in our galaxy – the Milky Way.The universe is far bigger than we could have imagine
The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It’s called a spiral galaxy because if you could view it from the top or bottom, it would look like a spinning pinwheel. The Sun is located on one of the spiral arms, about 25,000 light-years away from the center of the galaxy. Even if you could travel at the speed of light (300,000 kilometers, or 186,000 miles, per second), it would take you about 25,000 years to reach the middle of the Milky Way.Author: Shakir Essa
Like this:
Like Loading...
Related
-
Latest
 How To Get Super Rocket Radar Pokemon Go - Pokemon Fan Club
How To Get Super Rocket Radar Pokemon Go - Pokemon Fan ClubHow To Use The Rocket Radar In Pokmon Go free super team go rocket radar | pokemon go | rajlifeTo use the Rocket Radar, equip it from the items bag, then tap the icon in the upper right corn...
-
Next
 Pokemon GO: How to Get Super Rocket Radar - Prima Games
Pokemon GO: How to Get Super Rocket Radar - Prima GamesTeam GO has ramped things up in Pokemon GO and has begun invading the game with balloon attacks. Not only are they taking over different areas of the map, they’re also using Shadow Pokemon to accompli...
